| DOE:
Human-in-the-loop Sensing and Control for Commercial Building Energy Efficiency and Occupant Comfort |
DE-FOA-0001383 |
Project Introduction
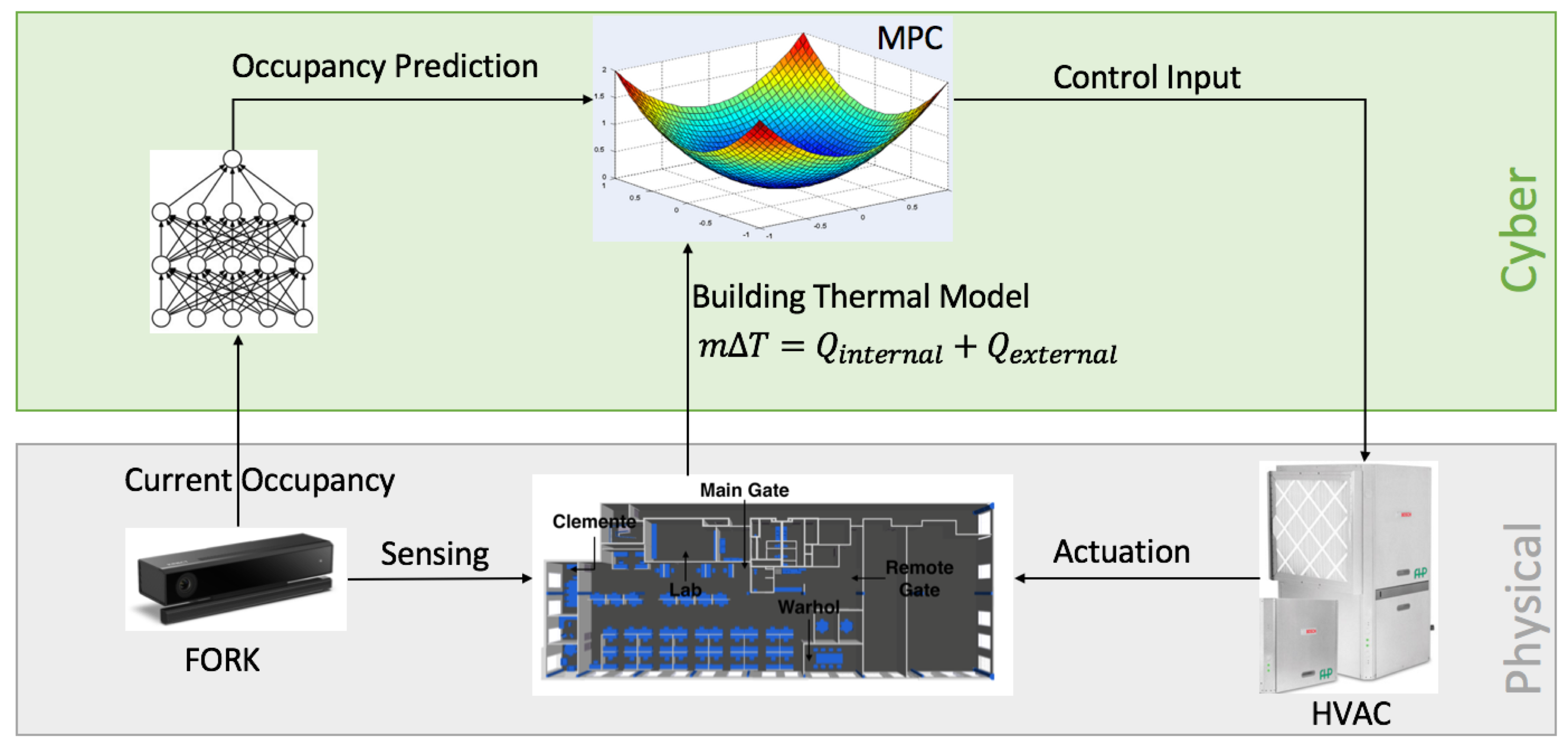
This project will design, implement, and evaluate a human-in-the-loop sensing and control system for energy efficiency of HVAC and lighting systems, which takes into account occupant comfort. Current HVAC systems operate by assuming maximum occupancy in each room, which leads to a significant energy waste. A novel lightweight solution will be developed to estimate number of occupants in an area accurately at real-time using a depth sensor. Body shape and height of the individuals will be sensed and used to control parameters of multi-stage HVAC system (set point, stage, duty cycle) for achieving better comfort as well as optimizing energy consumption. It will be integrated with existing sensing and actuation infrastructure, e.g., Volttron to collect large volume of real-world data for constructing models of number of occupants and occupant comfort. The solution brings humans into the loop by taking their feedback to improve model parameters and engage them to control HVAC and lighting systems to save energy. Carnegie Mellon University will leverage its long-standing relationship with Bosch Research to develop and test the solution at the CMU campus in realistic scenarios. Stony Brook University will help designing and implementation of the control aspect of the solution.